


"Big Data" refers to datasets which cannot be supported by traditional databases because they contain a very large volume data; with a variety of formats and structures; and data that moves at a high velocity. The term "Big Data" originated in 1997; became a hot term; and then cooled in use. Volume, variety and velocity are known as the three Vs of Big Data.
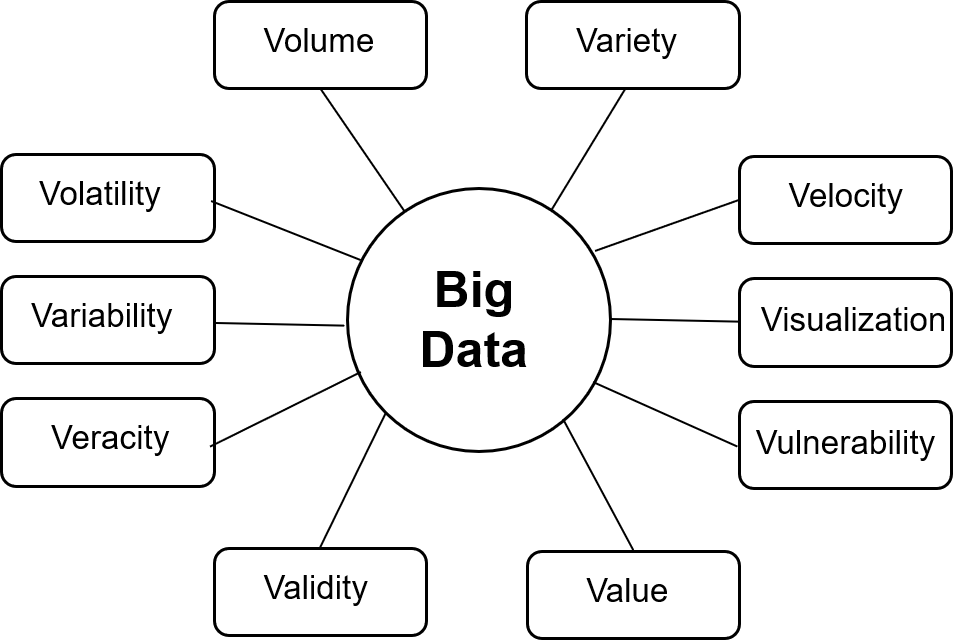
Since the three Vs were identified, more Vs have been brought forward. The 10 Vs of Big Data and Data Science are:
Big Data is important because it provides input to data science approaches like Machine Learning (ML), and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Use of these approaches have led to innovative breakthroughs. At time same time, the term Big Data is fading as large volumes of data are the norm rather than cutting edge exceptions.
Check out these Big Data links:
Infogoal.com is organized to help you gain mastery.
Examples may be simplified to facilitate learning.
Content is reviewed for errors but is not warranted to be 100% correct.
In order to use this site, you must read and agree to the
terms of use, privacy policy and cookie policy.
Copyright 2006-2020 by Infogoal, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
